KLISYRI®: Evaluated in a real-world study of patients and physicians
VIEW REAL WORLD RESULTSTirbanibulin (KLISYRI®) treatment showed effectiveness in AK management. Moreover, patients treated with tirbanibulin showed improvements in health-related quality of life (QoL) measures as early as Week 8, and both clinicians and patients reported tirbanibulin treatment convenience and high levels of treatment satisfaction.1,2
PROAK study overview
A real-world
study with
results at
24 weeks3
A real-world study with results at 24 weeks3
Patient- and Clinician-Reported Outcomes in Actinic Keratosis (PROAK) was an observational, single-arm, prospective, multicenter, Phase IV study among 300 adult patients with AK on the face or scalp who initiated treatment with tirbanibulin (per clinical judgment of the Site Investigator) in real-world clinical practices in the US as part of routine care.3
Patients and clinicians completed surveys and clinical assessments concerning the safety and effectiveness of tirbanibulin at baseline, Week 8 (timeframe for primary endpoints), and Week 24 (290 patients were included in the full analyses set).3
The primary endpoint was patient-reported QoL in terms of self-perceived AK symptoms and impact of AK on emotional well-being and functioning, as assessed by the Skindex-16 survey at Week 8. Additional endpoints included (not exclusively) tirbanibulin satisfaction as assessed by the Treatment Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9) and the Expert Panel Questionnaire (EPQ) at Week 8, treatment effectiveness assessed by Investigator’s Global Assessment (IGA) at Week 8, investigator rating of severity of photodamage at Weeks 8 and 24, frequency of documented adverse events (AEs), serious adverse events (SAEs), and local skin reactions (LSRs) during the first 8 weeks of the study observation period.
Limitations of the study include the potential for recall bias, reporting bias, selection bias, and other biases commonly seen in real-world and open-label studies. Approaches such as standardized study inclusion/exclusion criteria, consecutive sampling, and geographically diverse dermatology clinics with varied experience with topical field therapy were employed to minimize these biases.
The purpose of the PROAK study was to evaluate patient-reported outcomes (PROs) and clinician-reported outcomes (ClinROs) regarding efficacy and safety among adult patients with AKs on the face or scalp who were administered tirbanibulin in real-world community practices in the US.2
Data from both Week 8 and Week 24 are presented below.
Results from the PROAK study
REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE1-3
Patient- and Clinician-Reported Outcomes for Tirbanibulin effectiveness in Actinic Keratosis in Clinical Practice Across the United States (PROAK)1-3
Under real-world circumstances, both patients and clinicians reported high levels of treatment effectiveness as measured by IGA and a high degree of treatment satisfaction with tirbanibulin at Week 8 and Week 24 based on reported effectiveness, convenience, and global satisfaction.2,3
Tirbanibulin treatment also showed improvements in quality of life (QoL) measures at Week 8, based on changes in symptoms and functional impact from baseline.1,3
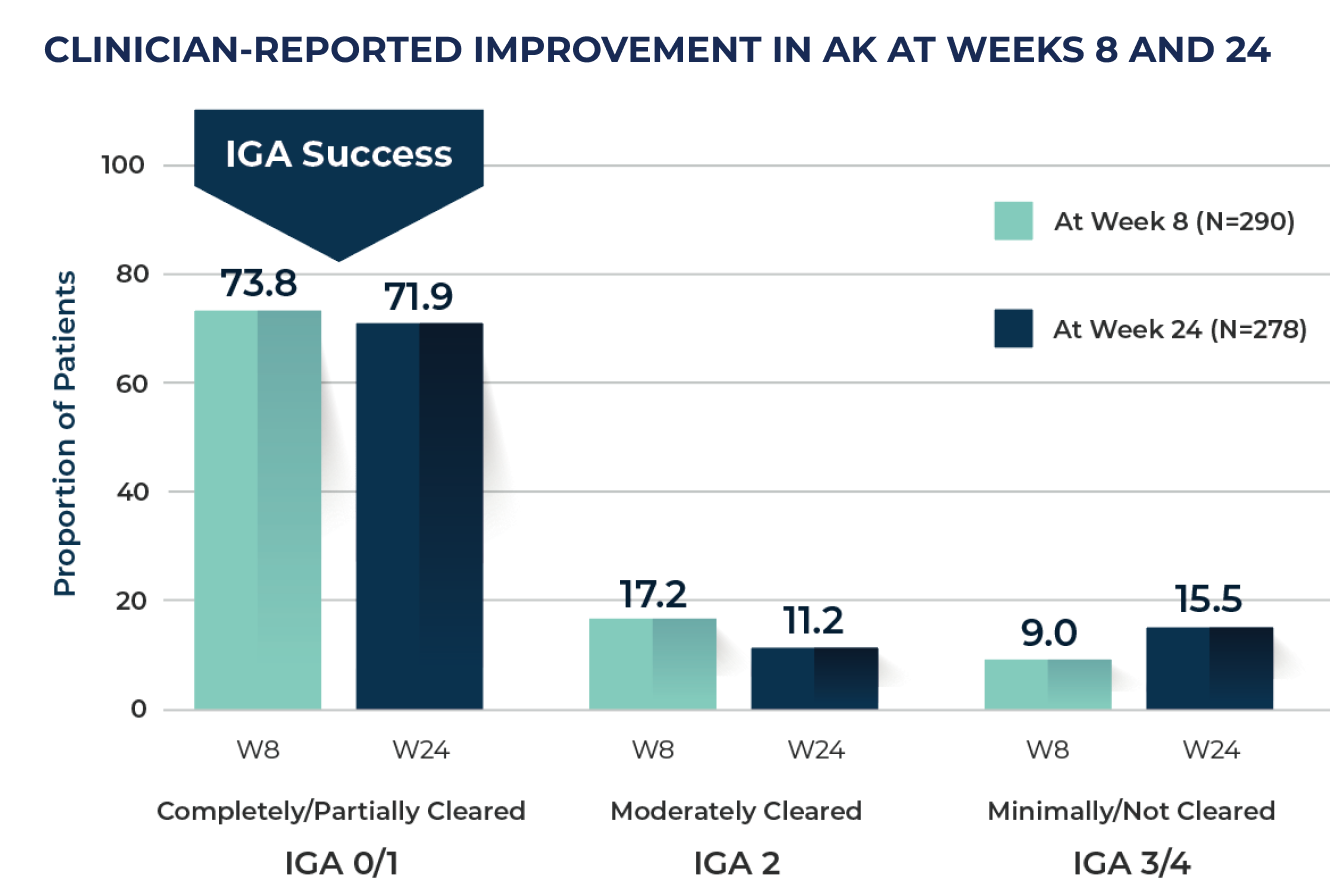
WEEK 8:
~74%
PATIENTS WERE CLEAR OR ALMOST CLEAR
WEEK 24:
~72%
PATIENTS WERE CLEAR OR ALMOST CLEAR
IGA: Investigator’s Global Assessment; W8: Week 8; W24: Week 24.
IGA success was defined as an IGA score of completely cleared (0) or partially cleared (1) in AK status in the treated area at Week 8.3
At Week 24, response categories of "don’t know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.2
CONCORDANT Patient and Clinician Satisfaction
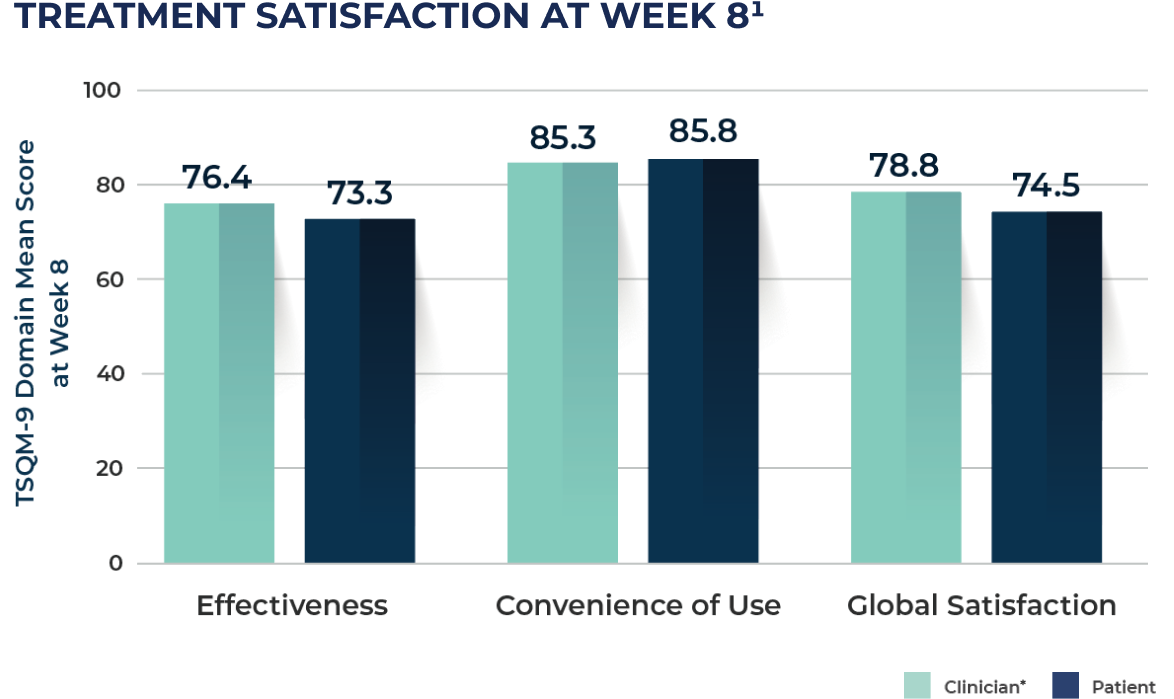
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
*Adapted from the patient version of the 9-item Treatment
Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9).
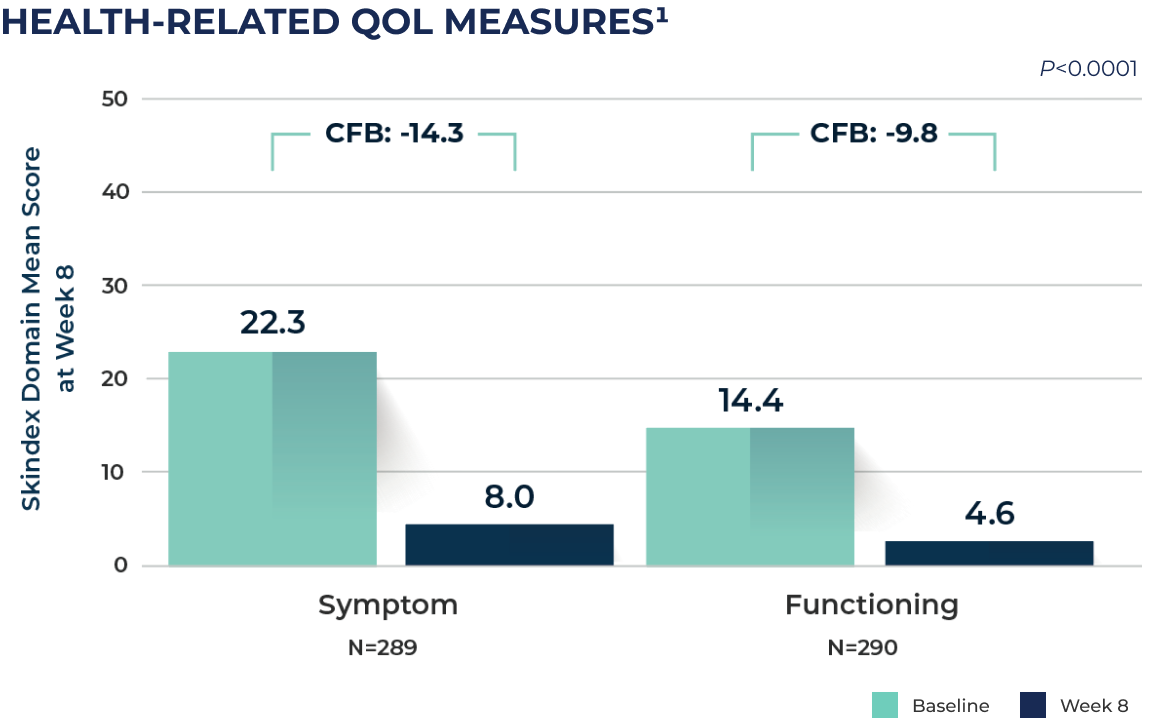
CFB: change from baseline; QoL: Quality of life.
The Skindex-16 survey was used to comprehensively assess the impact of tirbanibulin on health-related QoL.
"Symptom" domain consisted of four items: itching, burning, hurting, irritation.
"Functioning" domain consisted of five items: impact on interactions with others, desire to be with people, showing affection, daily activities, work, or other activities.
of patients and clinicians said they were somewhat or very likely to consider tirbanibulin to treat AK lesions in the future2
The results of PROAK
reinforced previously
published effectiveness,
safety, and tolerability of
tirbanibulin in the treatment
of AK of the face or scalp2,3
of patients and clinicians said they were somewhat or very likely to consider tirbanibulin to treat AK lesions in the future2
The results of PROAK
reinforced previously
published effectiveness,
safety, and tolerability of
tirbanibulin in the treatment
of AK of the face or scalp2,3
Results from the PROAK study
REAL-WORLD EVIDENCE1-3
Patient- and Clinician-Reported Outcomes for Tirbanibulin effectiveness in Actinic Keratosis in Clinical Practice Across the United States (PROAK)1-3
Under real-world circumstances, both patients and clinicians reported high levels of treatment effectiveness as measured by IGA and a high degree of treatment satisfaction with tirbanibulin at Week 8 and Week 24 based on reported effectiveness, convenience, and global satisfaction.2,3
Tirbanibulin treatment also showed improvements in quality of life (QoL) measures at Week 8, based on changes in symptoms and functional impact from baseline.1,3

IGA: Investigator’s Global Assessment; W8: Week 8; W24: Week 24.
IGA success was defined as an IGA score of completely cleared (0) or partially cleared (1) in AK status in the treated area at Week 8.3
At Week 24, response categories of "don’t know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.2
WEEK 8:
~74%
PATIENTS WERE CLEAR OR ALMOST CLEAR
WEEK 24:
~72%
PATIENTS WERE CLEAR OR ALMOST CLEAR
of patients and clinicians said they were somewhat or very likely to consider tirbanibulin to treat AK lesions in the future2
The results of PROAK
reinforced previously
published effectiveness,
safety, and tolerability of
tirbanibulin in the treatment
of AK of the face or scalp2,3
CONCORDANT Patient and
Clinician Satisfaction

Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
*Adapted from the patient version of the 9-item Treatment
Satisfaction Questionnaire for Medication (TSQM-9).

CFB: change from baseline; QoL: Quality of life.
The Skindex-16 survey was used to comprehensively assess the impact of tirbanibulin on health-related QoL.
"Symptom" domain consisted of four items: itching, burning, hurting, irritation.
"Functioning" domain consisted of five items: impact on interactions with others, desire to be with people, showing affection, daily activities, work, or other activities.
of patients and clinicians said they were somewhat or very likely to consider tirbanibulin to treat AK lesions in the future2
The results of PROAK
reinforced previously
published effectiveness,
safety, and tolerability of
tirbanibulin in the treatment
of AK of the face or scalp2,3
At Week 24, clinicians and patients were still highly satisfied with overall skin appearance and improvement in skin appearance and texture2‡
Rating of overall appearance of skin
Nearly 84% of clinicians and 78% of patients felt that the overall appearance of the skin showed improvement
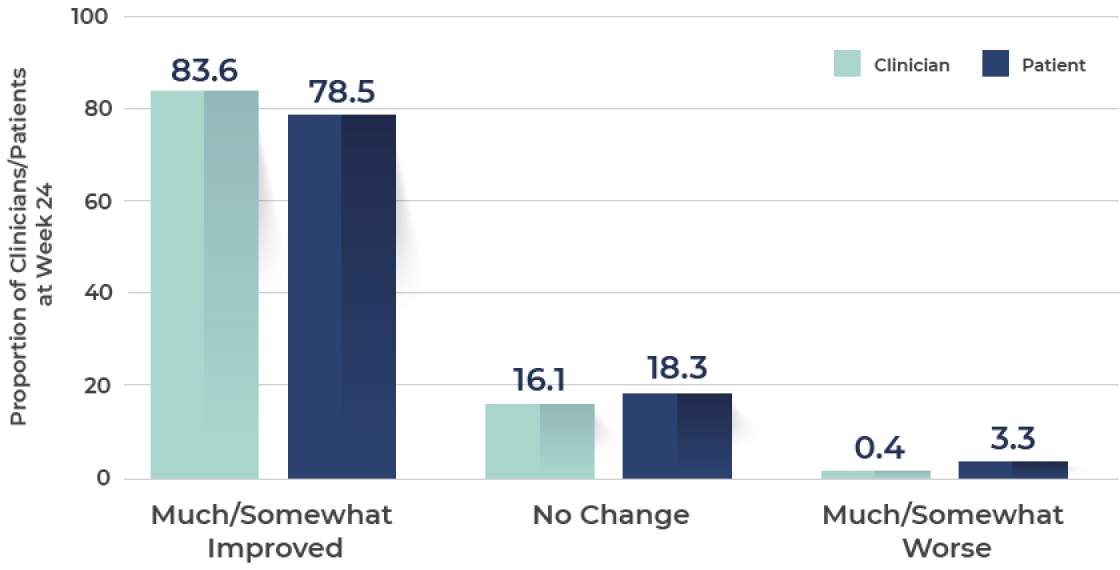
N=274.§
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
§At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
Rating of satisfaction with improvement in "how skin looks"
A high degree of patients and clinicians were extremely/very satisfied with how skin looked after treatment with tirbanibulin
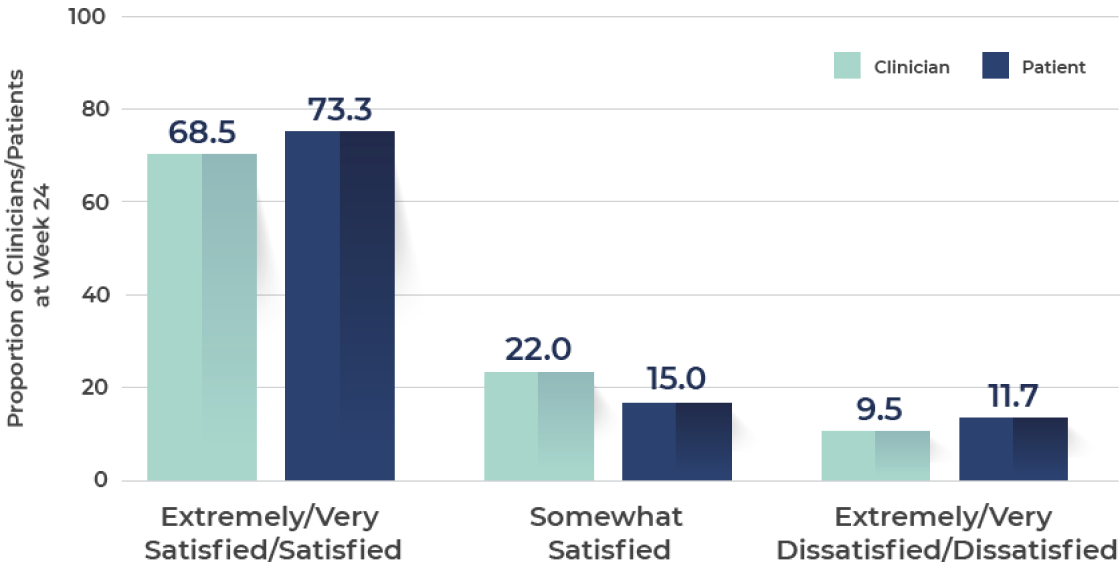
N=273.‖
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
‖At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
Rating of satisfaction with improvement in "skin texture"
Both patients and clinicians were extremely/very satisfied with the improvement in skin texture at Week 24
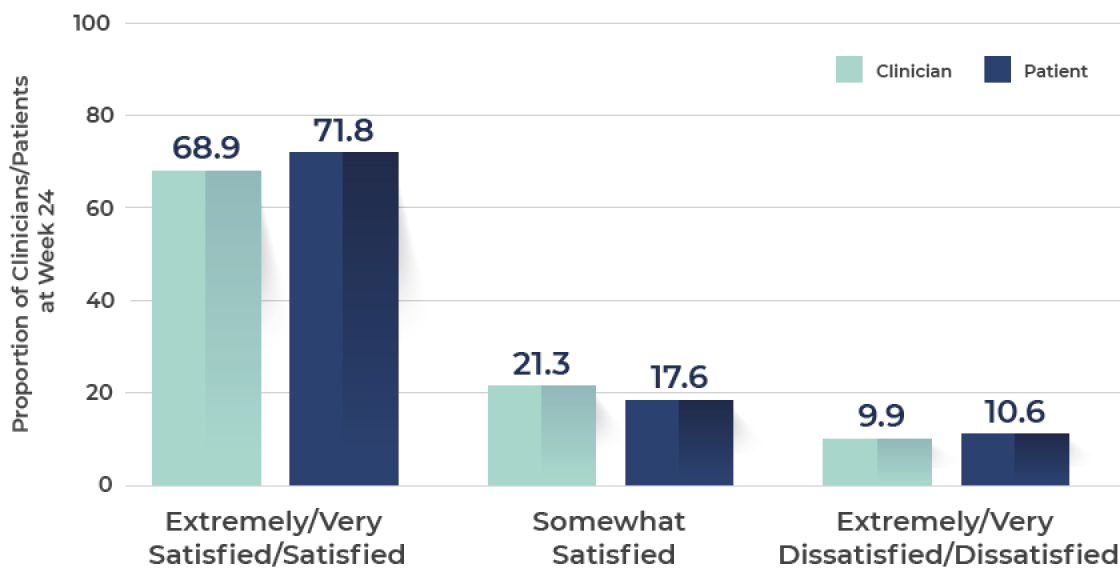
N=273.¶
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
¶At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
‡The PROAK study was funded by Almirall, and some of the study authors have affiliations with Almirall.
At Week 24, clinicians and patients were still highly satisfied with overall skin appearance and improvement in skin appearance and texture2‡
Rating of overall appearance of
skin
Rating of satisfaction with improvement in "how skin looks"
Rating of satisfaction with improvement in "skin texture"
Nearly 84% of clinicians and 78% of patients felt that the overall appearance of the skin showed improvement

N=274.§
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
§At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
A high degree of patients and clinicians were extremely/very satisfied with how skin looked after treatment with tirbanibulin

N=273.‖
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
‖At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
Both patients and clinicians were extremely/very satisfied with the improvement in skin texture at Week 24

N=273.¶
Ranging from 0 (least satisfaction) to 100 (most satisfaction).
¶At Week 24, response categories of "don't know/not applicable" were excluded from the analysis.
‡The PROAK study was funded by Almirall, and some of the study authors have affiliations with Almirall.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
INDICATION
KLISYRI is a microtubule inhibitor indicated for the topical field treatment of actinic keratosis on the face or scalp.
IMPORTANT SAFETY INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
Ophthalmic Adverse Reactions
KLISYRI may cause eye irritation. Avoid transfer of the drug into the eyes and to the periocular area during and after application. Wash hands immediately after application. If accidental exposure occurs, instruct patient to flush eyes with water and seek medical care as soon as possible.
Local Skin Reactions
Local skin reactions, including severe reactions (erythema, flaking/scaling, crusting, swelling, vesiculation/pustulation, and erosion/ulceration) in the treated area can occur after topical application of KLISYRI. Occlusion after topical application of KLISYRI is more likely to result in irritation. Avoid use until skin is healed from any previous drug, procedure, or surgical treatment.
ADVERSE REACTIONS
The most common adverse reactions (incidence ≥2%) were local skin reactions, application site pruritus, and application site pain.
Please see full Prescribing Information.
To report an adverse event or product complaint, call or email Medical Affairs and Customer Relations • Phone: 1-866-665-2782• Fax: 510-595-8183 •
Email: almirallmc@eversana.com
References: 1. Schlesinger T, Kircik L, Del Rosso J, et al. Clinician- and patient-reported outcomes with tirbanibulin 1% treatment for actinic keratosis in routine clinical practice across the US (PROAK Study). Skin 2023;7(3):771-787. 2. Schlesinger T, Kircik L, Lebwohl M, et al. Patient- and clinician-reported outcomes for tirbanibulin in actinic keratosis in clinical practice across the United States (PROAK). J Drugs Dermatol. 2024;23(5):338-346. doi:10.36849/JDD/8264 3. Data on file 2023. PROAK Study Final Report.